# 阿昌教你看懂SpringMVC执行流程
一、前言 Hello呀!!!阿昌又来也╰(°▽° )╯!!!
SpringMVC的执行流程大家应该都挺熟悉的,但是真的去debug源码的人应该算少数,这里阿昌一直都想自己记录一下debug-SpringMVC的执行流程源码,做一下总结,今天终于有机会记录一下SpringMVC执行流程
同样我还是建议打开源码一起debug看!!!
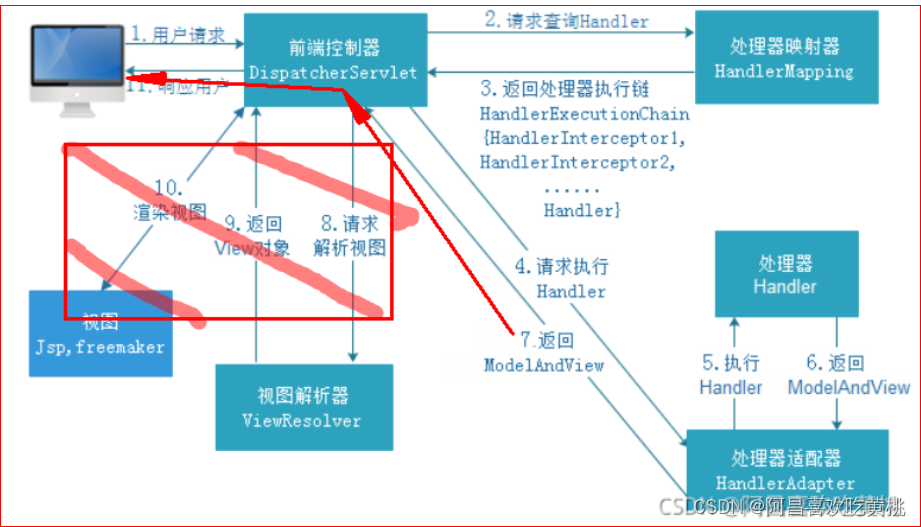
1、流程图
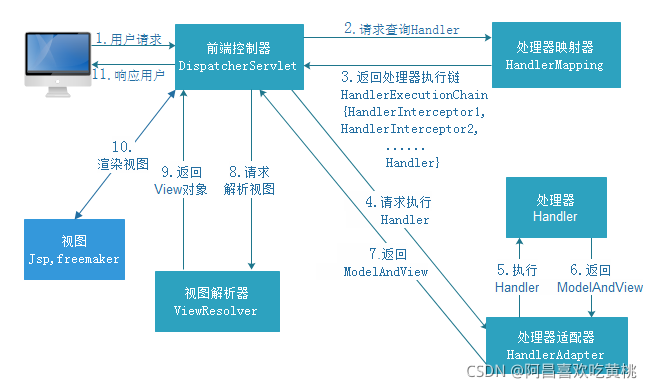
更详细一点 :
2、基于版本
SpringBoot:2.4.1
3、前置的测试代码 这里debug只涉及到controller和Interceptor拦截器,且端口在8080 (๑•̀ㅂ•́)و✧
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @RequestMapping("/test") @RestController public class TestController { @GetMapping("/123") public String test (@RequestParam String name, ServletResponse response) { System.out.println("name=" +name); System.out.println("response:" +response.isCommitted()); return "我是结果" ; } }
MyInterceptor拦截器
拦截器就涉及到了3个执行方法的执行顺序
preHandle()
postHandle()
afterCompletion()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("MyInterceptor.preHandle" ); System.out.println("response:" +response.isCommitted()); return true ; } @Override public void postHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("MyInterceptor.postHandle" ); System.out.println("response:" +response.isCommitted()); } @Override public void afterCompletion (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("MyInterceptor.afterCompletion" ); System.out.println("response:" +response.isCommitted()); } }
二、正文 这里我们启动服务,并用浏览器请求:http://localhost:8080/test/123?name=阿昌 (。・∀・)ノ゙
我们都知道对于SpringBoot中是自带Tomcat服务器的组件的,当一个请求发来,会被Tomcat处理,并转交给SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet类来做接下来的处理,他在SpringMVC中非常的重要,起着流程执行骨架的作用。
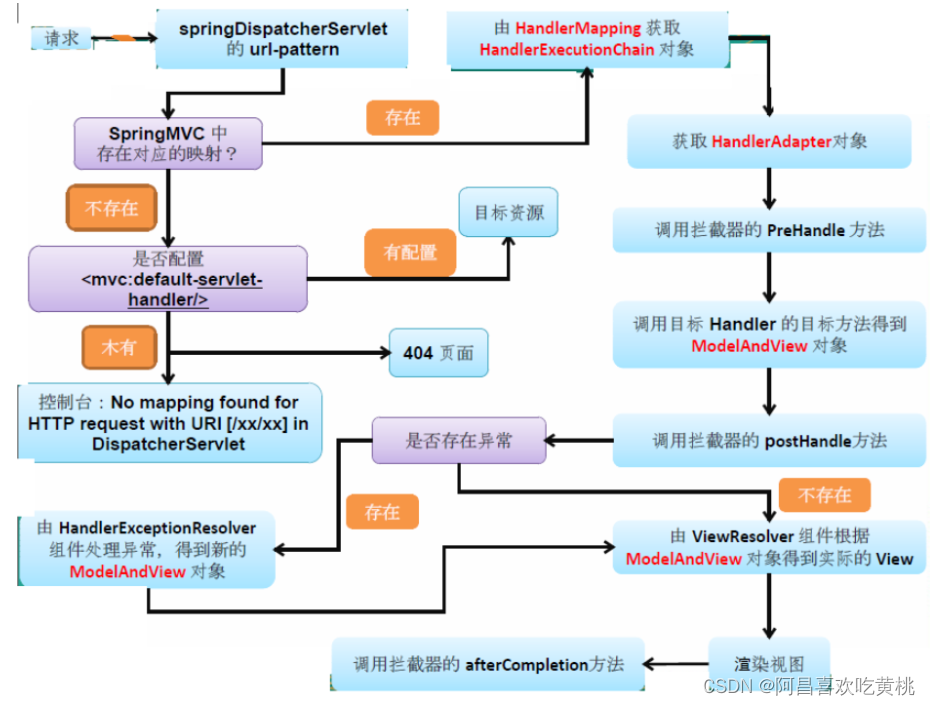
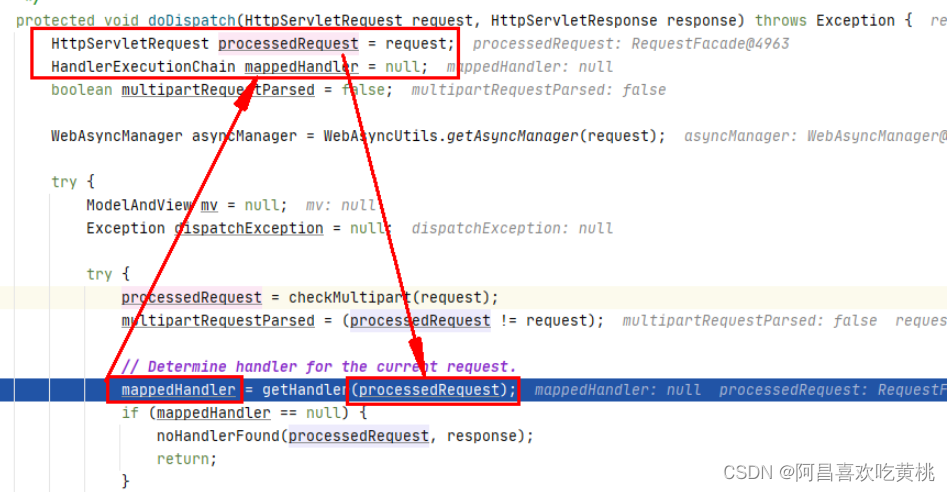
1、doDispatch 那首先Tomcat会经过流转调用去执行DispatcherServlet.doDispatch()方法
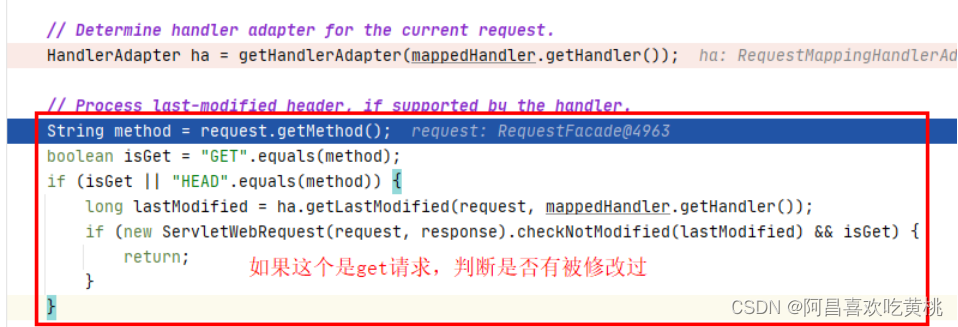
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 protected void doDispatch (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null ; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false ; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null ; Exception dispatchException = null ; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null ) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return ; } HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET" .equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD" .equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest (request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return ; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return ; } mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return ; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { dispatchException = new NestedServletException ("Handler dispatch failed" , err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException ("Handler processing failed" , err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { if (mappedHandler != null ) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
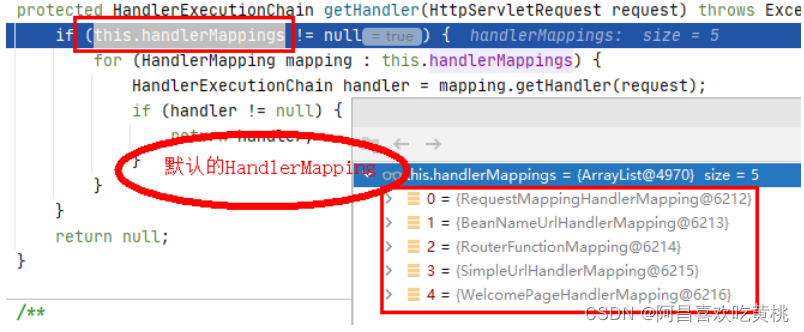
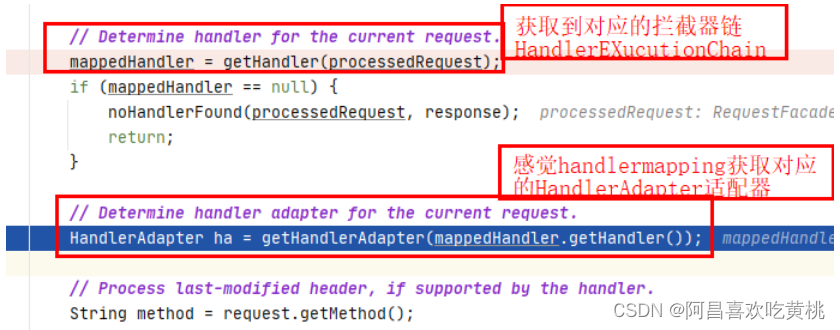
2、getHandler 经过一些的初始化后,首先会去执行getHandler()方法,去寻找对应可以去处理这个请求的mappedHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler (HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this .handlerMappings != null ) { for (HandlerMapping mapping : this .handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null ) { return handler; } } } return null ; }
mapping.getHandler(request)
mapping.getHandler(request)拿到的是被包装后的handlerMapping,也就是HandlerExecutionChain
handlerMapping处理器
对应的拦截器
这次的请求request
封装成HandlerExecutionChain
获取handlerMapping
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Override protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal (HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request); this .mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null ); } finally { this .mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } }
4、小总结 执行这里就会遍历所有this.handlerMappings,获取请求的uri和请求,拿到对应能够处理这次请求的handlerMapping,并将拿到:↓
handlerMapping处理器
对应的拦截器
这次的请求request
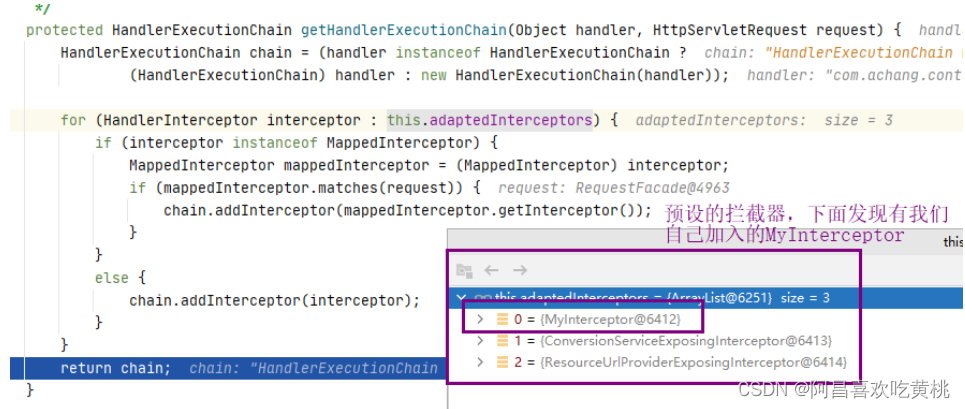
包装成一个HandlerExecutionChain。
5、getHandlerAdapter() 上面我们获取到的对应的HandlerExecutionChain拦截器链(处理器handlermapping+拦截器链+这次请求)。
接下来就要获取对应这个handlermapping对应的的适配器HandlerAdapter
里面的逻辑也很简单,遍历所有的handlerAdapter,看看哪个可以处理个handlerMapping,找到后返回
6、判断如果是get请求,是否被修改
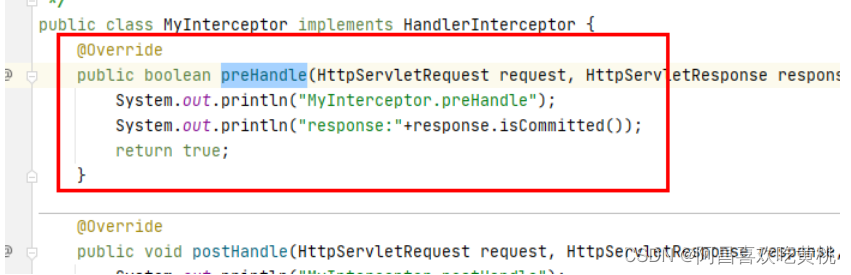
7、applyPreHandle() 这里就是上面流程图的执行器链中的一个执行时机之一applyPreHandle,他会去执行所有拦截器链中的每个拦截的applyPreHandle()方法
我们自定义的拦截器MyInterceptor.preHandle
执行所有拦截器链中的每个拦截的applyPreHandle()方法
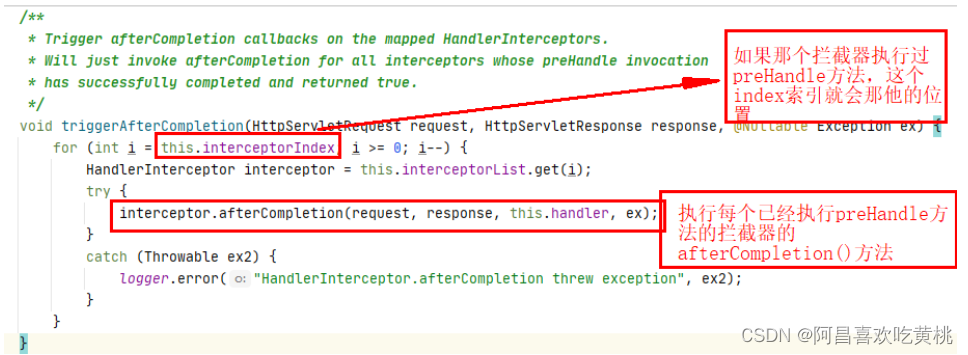
每执行成功一个this.interceptorIndex就会给赋上i的值(拦截器变量的索引)
这里因为上面每次执行preHandle都会记录一下拦截器变量的索引
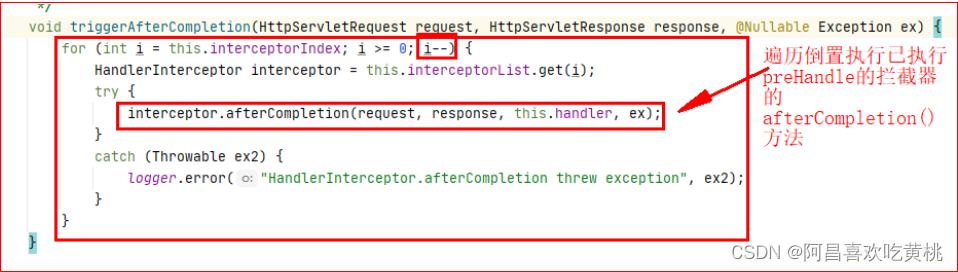
所以如果有一个preHandle执行返回了false,那么这里就会倒置的去执行已经执行的拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
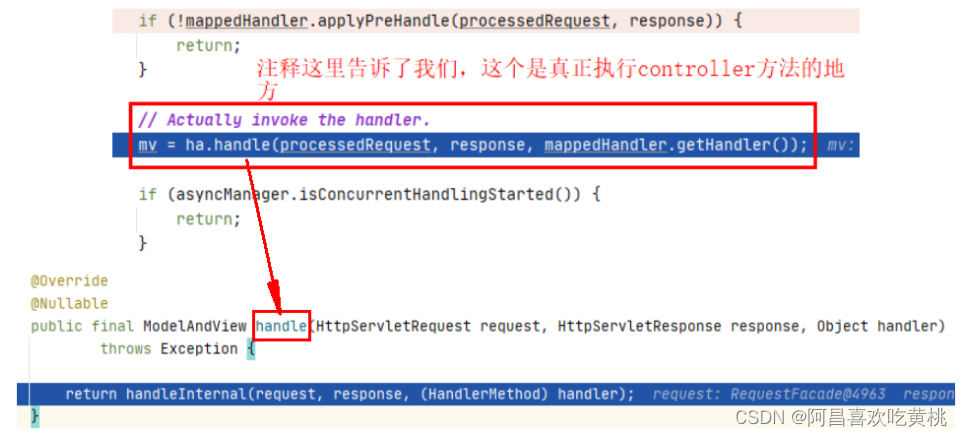
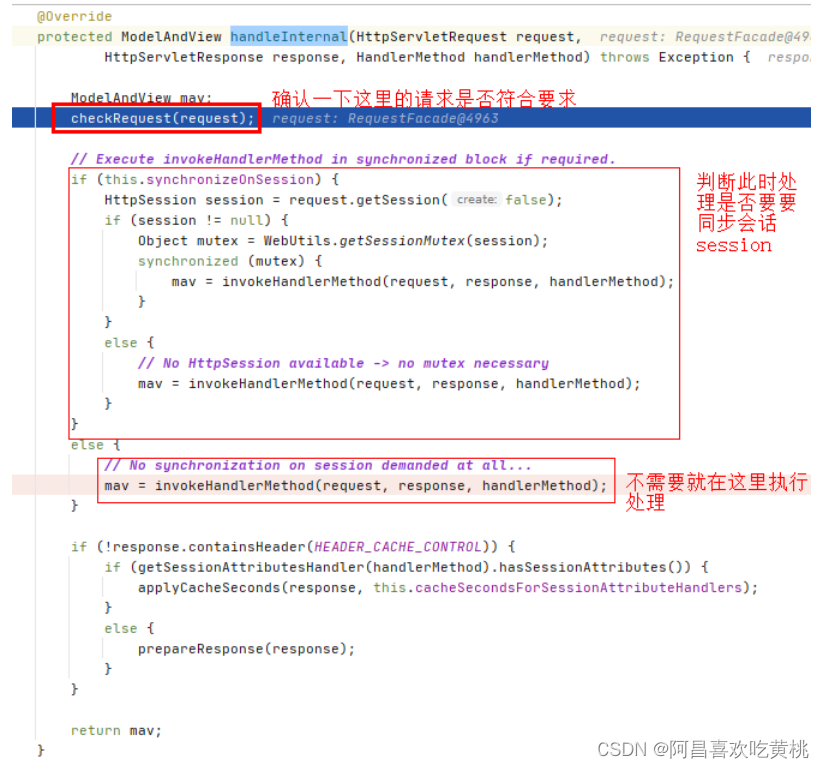
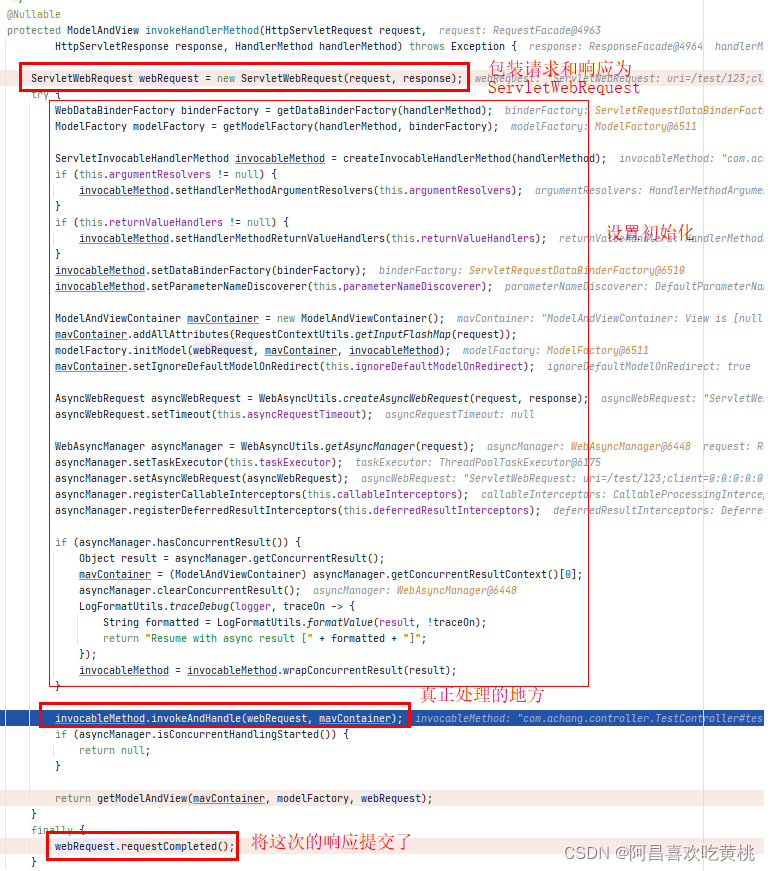
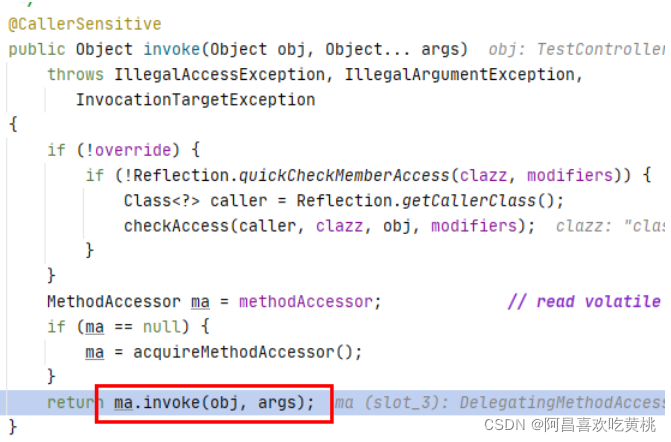
8、handle 1 ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
这里是真正执行我们这次请求处理的controller对应的方法
==那阿昌这里就好奇了,他是如何执行,并拿到对应的结果的,这个结果封装在哪里???==
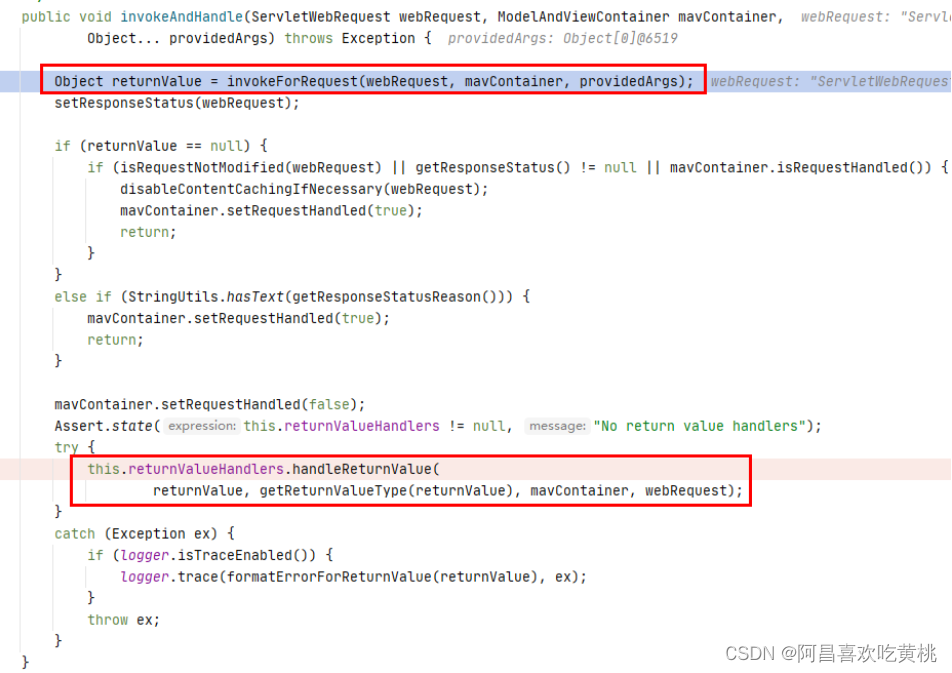
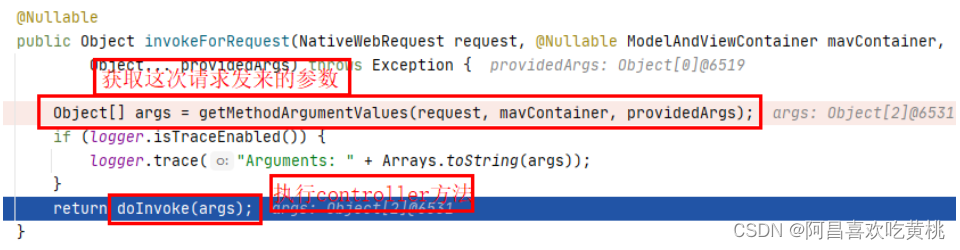
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Nullable public Object invokeForRequest (NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args)); } return doInvoke(args); }
这里就是controller的代理了,对应的代理设计模式
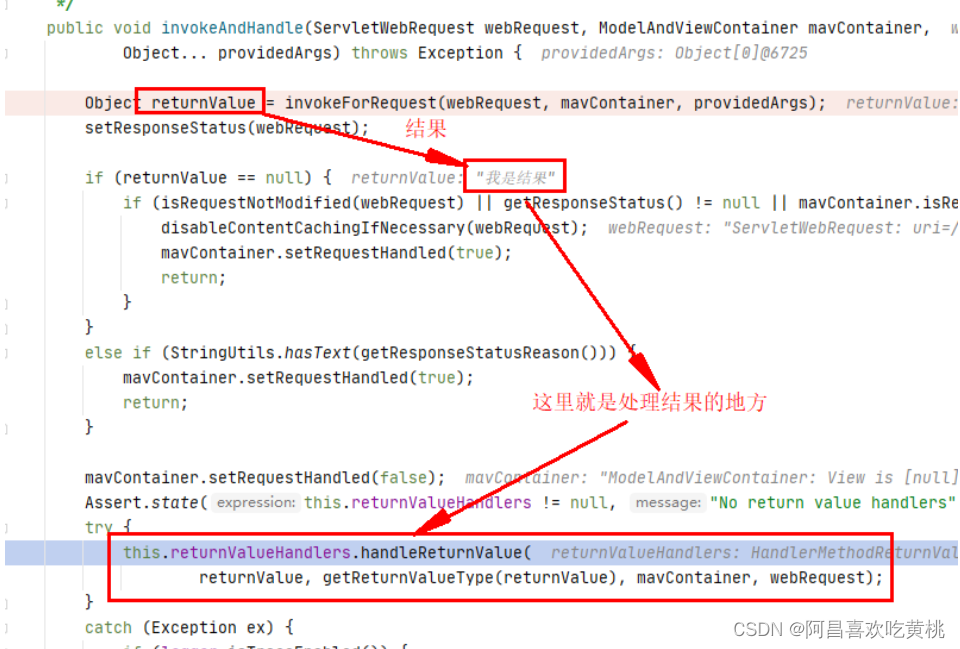
==那上面拿到执行了controller的方法后,拿到的结果是如何处理的呢?==
writeWithMessageConverters
将处理响应的结果,写入响应中,这个方法很长,对应与servletHttp响应 响应的介绍
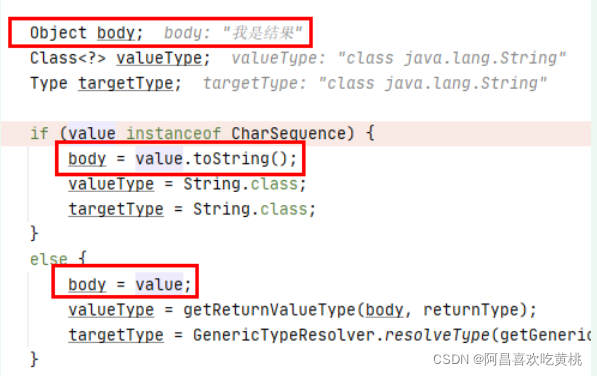
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 protected <T> void writeWithMessageConverters (@Nullable T value, MethodParameter returnType, ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage, ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException { Object body; Class<?> valueType; Type targetType; if (value instanceof CharSequence) { body = value.toString(); valueType = String.class; targetType = String.class; } else { body = value; valueType = getReturnValueType(body, returnType); targetType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveType(getGenericType(returnType), returnType.getContainingClass()); } if (isResourceType(value, returnType)) { outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_RANGES, "bytes" ); if (value != null && inputMessage.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.RANGE) != null && outputMessage.getServletResponse().getStatus() == 200 ) { Resource resource = (Resource) value; try { List<HttpRange> httpRanges = inputMessage.getHeaders().getRange(); outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.PARTIAL_CONTENT.value()); body = HttpRange.toResourceRegions(httpRanges, resource); valueType = body.getClass(); targetType = RESOURCE_REGION_LIST_TYPE; } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_RANGE, "bytes */" + resource.contentLength()); outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE.value()); } } } MediaType selectedMediaType = null ; MediaType contentType = outputMessage.getHeaders().getContentType(); boolean isContentTypePreset = contentType != null && contentType.isConcrete(); if (isContentTypePreset) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Found 'Content-Type:" + contentType + "' in response" ); } selectedMediaType = contentType; } else { HttpServletRequest request = inputMessage.getServletRequest(); List<MediaType> acceptableTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request); List<MediaType> producibleTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, targetType); if (body != null && producibleTypes.isEmpty()) { throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException ( "No converter found for return value of type: " + valueType); } List<MediaType> mediaTypesToUse = new ArrayList <>(); for (MediaType requestedType : acceptableTypes) { for (MediaType producibleType : producibleTypes) { if (requestedType.isCompatibleWith(producibleType)) { mediaTypesToUse.add(getMostSpecificMediaType(requestedType, producibleType)); } } } if (mediaTypesToUse.isEmpty()) { if (body != null ) { throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException (producibleTypes); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No match for " + acceptableTypes + ", supported: " + producibleTypes); } return ; } MediaType.sortBySpecificityAndQuality(mediaTypesToUse); for (MediaType mediaType : mediaTypesToUse) { if (mediaType.isConcrete()) { selectedMediaType = mediaType; break ; } else if (mediaType.isPresentIn(ALL_APPLICATION_MEDIA_TYPES)) { selectedMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM; break ; } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using '" + selectedMediaType + "', given " + acceptableTypes + " and supported " + producibleTypes); } } if (selectedMediaType != null ) { selectedMediaType = selectedMediaType.removeQualityValue(); for (HttpMessageConverter<?> converter : this .messageConverters) { GenericHttpMessageConverter genericConverter = (converter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter ? (GenericHttpMessageConverter<?>) converter : null ); if (genericConverter != null ? ((GenericHttpMessageConverter) converter).canWrite(targetType, valueType, selectedMediaType) : converter.canWrite(valueType, selectedMediaType)) { body = getAdvice().beforeBodyWrite(body, returnType, selectedMediaType, (Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter <?>>) converter.getClass(), inputMessage, outputMessage); if (body != null ) { Object theBody = body; LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> "Writing [" + LogFormatUtils.formatValue(theBody, !traceOn) + "]" ); addContentDispositionHeader(inputMessage, outputMessage); if (genericConverter != null ) { genericConverter.write(body, targetType, selectedMediaType, outputMessage); } else { ((HttpMessageConverter) converter).write(body, selectedMediaType, outputMessage); } } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Nothing to write: null body" ); } } return ; } } } if (body != null ) { Set<MediaType> producibleMediaTypes = (Set<MediaType>) inputMessage.getServletRequest() .getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE); if (isContentTypePreset || !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(producibleMediaTypes)) { throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException ( "No converter for [" + valueType + "] with preset Content-Type '" + contentType + "'" ); } throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException (this .allSupportedMediaTypes); } }
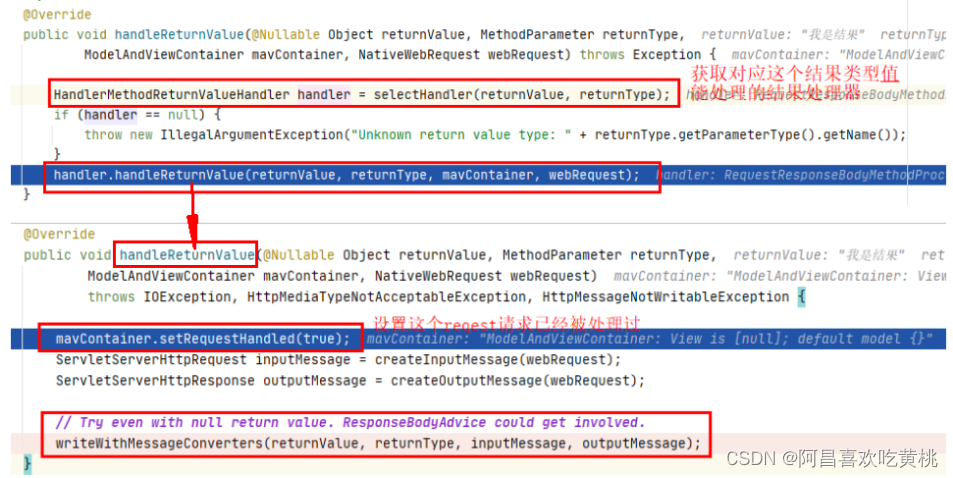
重要的部分在:
outputMessage:上面封装的webRequest中拿到的响应输出
1 2 ((HttpMessageConverter) converter).write(body, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
t:就是我们的结果“我是结果”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Override public final void write (final T t, @Nullable MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException { final HttpHeaders headers = outputMessage.getHeaders(); addDefaultHeaders(headers, t, contentType); if (outputMessage instanceof StreamingHttpOutputMessage) { StreamingHttpOutputMessage streamingOutputMessage = (StreamingHttpOutputMessage) outputMessage; streamingOutputMessage.setBody(outputStream -> writeInternal(t, new HttpOutputMessage () { @Override public OutputStream getBody () { return outputStream; } @Override public HttpHeaders getHeaders () { return headers; } })); } else { writeInternal(t, outputMessage); outputMessage.getBody().flush(); } }
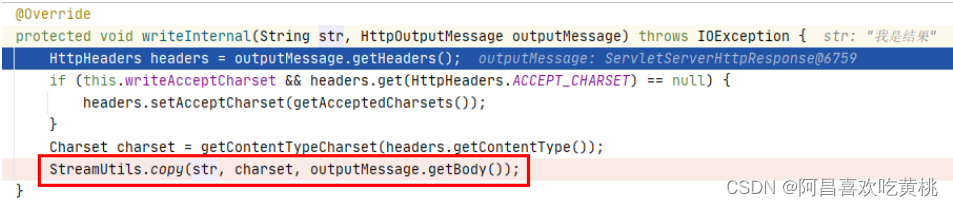
==他是如何写入outputMessage的呢?==
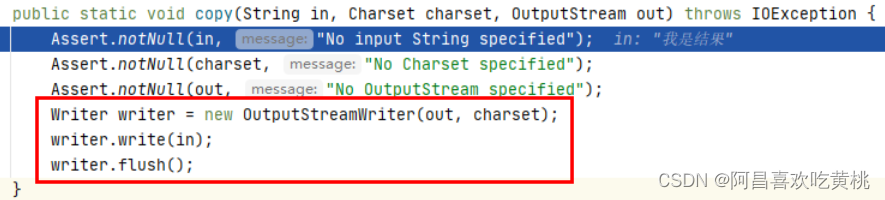
将t写入到outputMessage
就直接通过OutputStreamWriter直接调用write写入in也就是结果,最后flush刷新
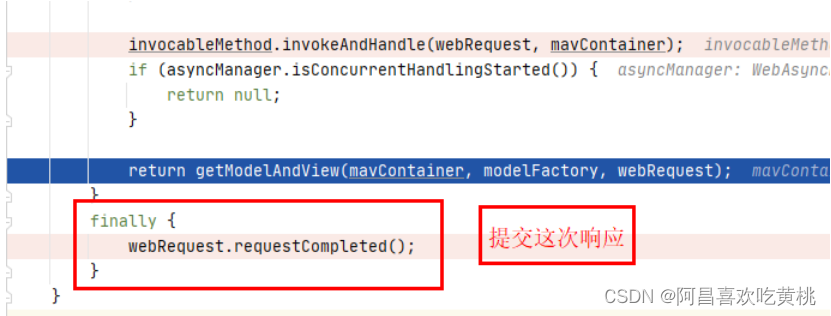
执行完写入响应结果后,他就会提交这次响应,什么是 提交响应呢?介绍:响应提交
9、小总结
上面我们拿到对应的HandlerExecutionChain拦截器链
这里包含:↓
处理器handlermapping
拦截器链
这次请求
从HandlerExecutionChain拦截器链到拿到对应的handlerMapping
根据handlerMapping,去获取对应的HandlerAdapter的处理器对应的适配器
判断请求方式是否是get,如果是就判断是否被修改过
遍历所有的拦截器链,执行每个applyPreHandle()
每次执行都记录执行的拦截器链遍历索引
如果有一个applyPreHandle返回false,就去导致执行triggerAfterCompletion,去执行倒置每一个已经执行applyPreHandle()方法的拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
再通过适配器执行真正处理这次请求的controller方法handle,返回ModelAndView
(==这里我们不是jsp,所以肯定必然没有ModelAndView对应,就肯定为null==)
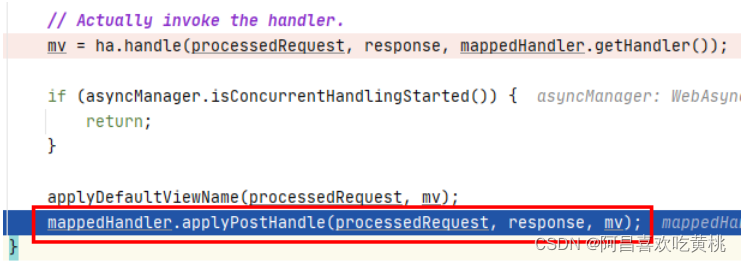
10、applyPostHandle()
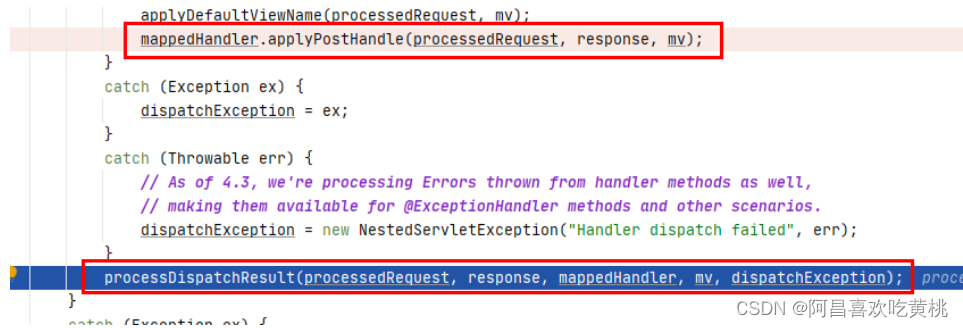
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return ; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
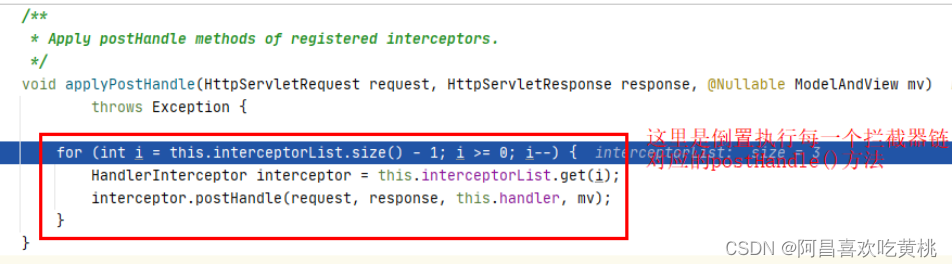
倒置去执行每个拦截器链中每个拦截的applyPostHandle()方法
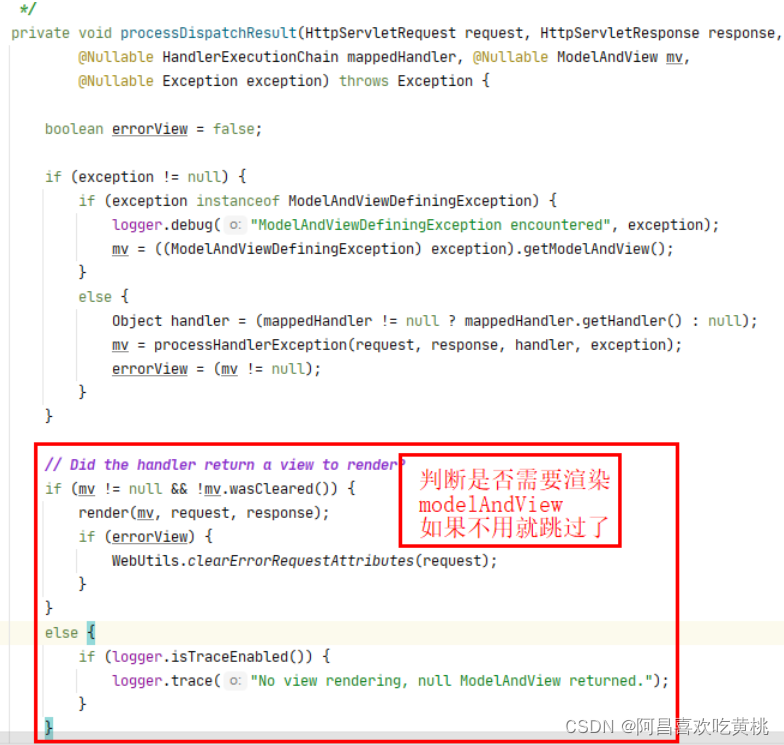
11、processDispatchResult() 在processDispatchResult()方法中,会做一些收尾的工作
这里会判断是否需要去渲染视图ModelAndView,因为我们这里是通过json响应返回,必然是没有modelAndView对象
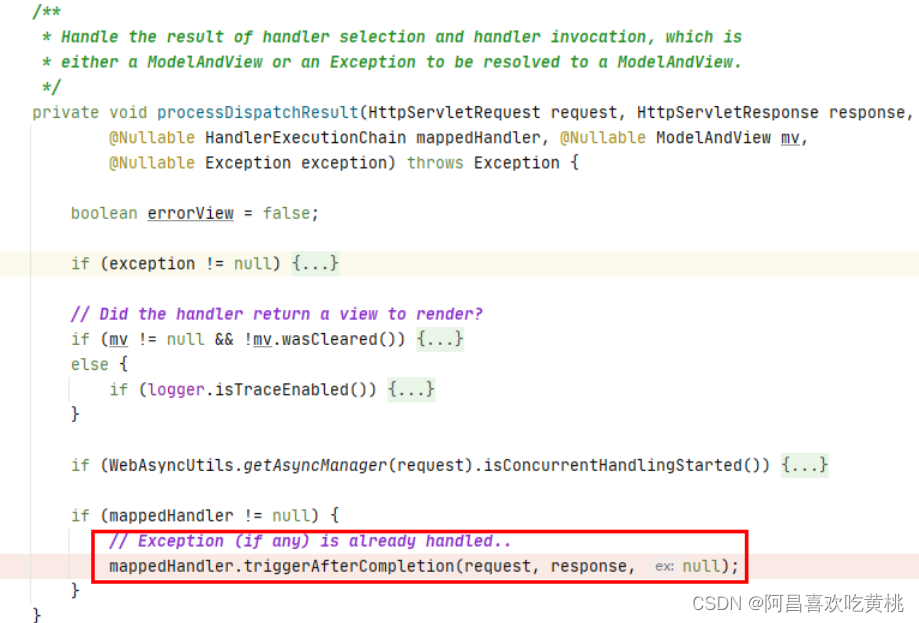
去执行triggerAfterCompletion(),这里上面已经出现过,也就是去执行已经执行过preHandle拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
这里会倒置执行已经执行过preHandle()方法的拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
12、小总结
执行适配器对应的handle()方法也就是对应的controller的方法后,会返回ModelAndView
判断当前请求的所选处理程序是否选择处理异步处理
给对应返回的ModelAndView对象赋予默认名
倒置去执行每个拦截器链中每个拦截的applyPostHandle()方法
执行processDispatchResult()做收尾工作
去执行triggerAfterCompletion(),这里上面已经出现过,也就是去执行已经执行过preHandle拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
三、总结
执行这里就会遍历所有this.handlerMappings,获取请求的uri和请求,拿到对应能够处理这次请求的handlerMapping,并将拿到:↓
handlerMapping处理器
对应的拦截器
这次的请求request
包装成一个HandlerExecutionChain。
从HandlerExecutionChain拦截器链到拿到对应的handlerMapping
根据handlerMapping,去获取对应的HandlerAdapter的处理器对应的适配器
判断请求方式是否是get,如果是就判断是否被修改过
遍历所有的拦截器链,执行每个applyPreHandle()
每次执行都记录执行的拦截器链遍历索引
如果有一个applyPreHandle返回false,就去导致执行triggerAfterCompletion,去执行倒置每一个已经执行applyPreHandle()方法的拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
再通过适配器执行真正处理这次请求的controller方法handle,返回ModelAndView
(==这里我们不是jsp,所以肯定必然没有ModelAndView对应,就肯定为null==)
执行适配器对应的handle()方法也就是对应的controller的方法后,会返回ModelAndView
判断当前请求的所选处理程序是否选择处理异步处理
给对应返回的ModelAndView对象赋予默认名
倒置去执行每个拦截器链中每个拦截的applyPostHandle()方法
执行processDispatchResult()做收尾工作
判断是否有ModelAndView,有就渲染,没有执行下面的
去执行triggerAfterCompletion(),这里上面已经出现过,也就是去执行已经执行过preHandle拦截器的afterCompletion()方法
四、结尾 以上SpringMVC的流程就执行完毕了,因为不涉及到jsp的流程,所有DispatcherServlet就拿到上面处理的响应结果,因为ModelAndView为空,就没请求渲染视图了,直接响应tomcat,然后tomcat就返回给响应请求了
以上就是这次的全部内容,感谢你能看到这里(๑ˉ∀ˉ๑)!!!

![image]()



![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3QukQUNv-1639907575817)(../AppData/Roaming/Typora/typora-user-images/image-20211219165433034.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/845c634aeafe46a1ae8379056d9ffb5f.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA6Zi_5piM5Zac5qyi5ZCD6buE5qGD,size_18,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)

![image]()